Job Displacement Due to Automation: Separating Fact from Fiction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to shape the corporate world, with Generative AI (GenAI) taking center stage. This subset of AI can generate new content and mimic human cognition, prompting consequential discussions about AI's impact on jobs as we know them.
Will it augment or automate jobs? How will this shift affect industries, enterprises, and employees? These critical questions are fundamental to understanding the transformation of today's workforce.
New Report: 2025 AI Job Market Trends
Automation vs. Augmentation: How AI Impacts Job Displacement
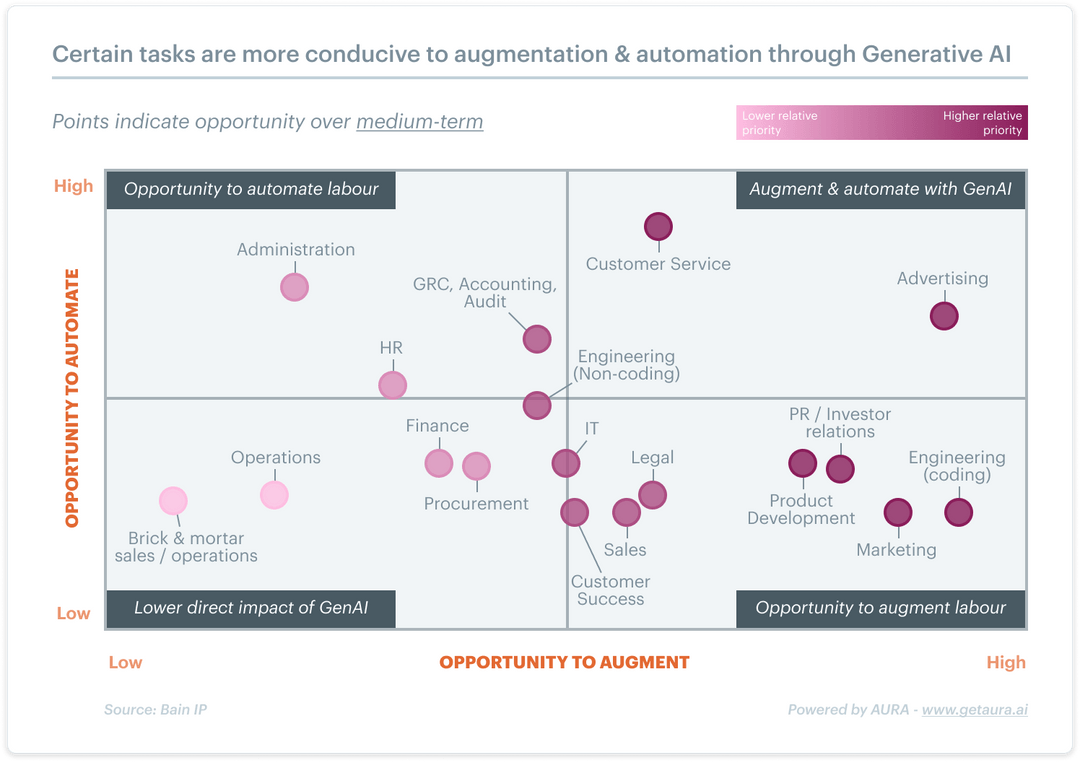
Businesses have an opportunity to utilize GenAI to bolster their business value. GenAI presents them with the potential to successfully optimize workforce deployment by analyzing each task and role. However, it necessitates understanding how AI could augment human capabilities or automate tasks in various sectors to streamline productivity.
AI technologies vary in terms of how they contribute to augmentation and automation. Augmentation empowers the human workforce by integrating AI to amplify their performance. Simultaneously, automation replaces humans' handling of repetitive tasks, potentially leading to job displacement. GenAI holds substantial prospects in bolstering job roles where creativity, problem-solving, and empathy – innately human skills – are critical.
Balancing Automation with a Human Touch in Critical Industries
-
Counseling and therapy. While AI can manage preliminary assessments and is beginning to emulate empathy, it cannot yet substitute the human connection required for holistic counseling services.
-
Advertising and marketing. While AI can automate several tasks, such as ad placement, content creation, and analytics, creative aspects require emotion and a unique human touch.
-
Healthcare, social work, and teaching. Even with AI administering diagnostics or administrative tasks, humans' empathy and understanding cannot be automated within these sectors.
-
Doctors and nurses. AI aids by delivering information, but judgment and intuition needed in healthcare practices are uniquely human attributes necessary to satisfy healthcare legal and regulatory requirements.
AI will undoubtedly change the work landscape. Our creativity, problem-solving abilities, and empathy will continue to be vital. We're not being replaced but entering a new era where our skills are even more valuable.
Departments like engineering, marketing, and PR/investor relations can substantially benefit from GenAI enhancement, leading to increased efficiency. On the other hand, functions like accounting, administration, and HR may undergo potential automation for manual and repetitive tasks.
As AI progresses, the need for reskilling and upskilling initiatives will become crucial. Individuals need access to training programs to adapt to the dynamic workplace environment. This adaptability will become a critical skill in the era of AI, ensuring that employees remain relevant in the ever-changing job market.
Job Displacement Due to AI: Myths vs. Reality
Concerns about Generative AI’s potential to automate jobs and displace workers are significant. This fear is palpable, especially in industries where routine tasks dominate. However, this narrative may be overly pessimistic.
Automation may indeed lead to job losses in some industries. On the other hand, automation can potentially create new industries and job opportunities, especially in advanced economies. Therefore, investing in retraining and upskilling displaced workers and equipping them with skills that will be valuable in the new job markets is imperative.
Also, job displacement caused by automation only affects some industries equally. Some sectors will be more impacted, leading to economic inequality, meaning policymakers must work with industry leaders to establish suitable transition measures.
Another misconception is that AI, specifically artificial general intelligence, will lead to a bleak future where machines rule the world, and humans are left to fend for themselves. AI development thus far has been limited to narrow use cases and is a tool that can be steered towards social and environmental issues.
Reskilling Revolution: Empowering the Workforce for an AI-Driven Future
As Generative AI (GenAI) redefines industries and reshapes the workforce, a pivotal focus must be placed on reskilling and upskilling initiatives. The speed at which AI is being adopted demands an equally swift response to ensure employees are equipped to thrive in this new era. The “Reskilling Revolution” is not just a corporate responsibility but an economic imperative.
Reskilling: A Strategic Necessity
AI’s integration into the workplace doesn’t just replace tasks—it transforms them. Roles across industries now demand a hybrid skill set, where technical aptitude meets creativity, emotional intelligence, and strategic thinking. For instance:
-
Healthcare professionals are adapting to AI diagnostic tools by developing skills in data interpretation and patient-focused communication.
-
Finance teams are embracing AI-driven analytics platforms, shifting their focus from manual data entry to predictive financial modeling.
-
Marketing professionals are learning to complement AI-generated content with human insight, ensuring that creativity remains authentic and emotionally resonant.
Organizations need to move beyond traditional training models and invest in continuous learning programs tailored to the AI age. This includes partnerships with educational institutions, micro-credentialing initiatives, and on-the-job training programs designed to close skill gaps in real time.
The Role of Public-Private Collaboration
Governments and businesses must collaborate to ensure that workers are not left behind in this shift. Public-private partnerships can play a critical role in funding large-scale reskilling programs, particularly for vulnerable industries where automation poses the greatest risks. Policymakers must also consider incentives, such as tax benefits for companies that prioritize workforce development and training.
Generative AI: From Job Displacement to Workforce Transformation
On the optimistic side, AI has the potential to empower human workers, making them more productive, efficient, and effective - this is referred to as augmentation. By collaborating with AI tools, workers can delegate repetitive and mundane tasks, focus more on their jobs' complex and creative aspects, and thus produce similar or better outputs while experiencing enhanced job satisfaction.
*Special thanks to Bain’s Gene Rapoport and Richard Lichtenstein for their materials and support in this article.
At the core of generative AI lies the ability to learn directly from examples rather than relying on manually crafted algorithms. Unlike traditional automation techniques, generative AI can create outputs based on specific input criteria. This opens up possibilities for organizations to automate more complex tasks that were previously beyond the reach of traditional automation.
Real-World Applications of AI-Driven Automation
Take the app SeekOut as an example. It's an AI-powered recruitment tool that supports recruitment professionals to contact potential candidates in a personalized way, allowing significantly more time to be spent on later-stage candidates where more excellent value can be achieved. Similarly, AI-enhanced automation tools in Finance departments can accelerate financial planning, cash flow operations, and payroll/tax processes.
Generative AI can revolutionize the way businesses process and interpret data. Generative AI can eliminate manual errors and improve speed and efficiency by automating data processing. Moreover, AI-powered data analysis can identify patterns and insights that may have been overlooked or would have taken humans much longer to determine.
Another area where Generative AI holds excellent potential is workflow and talent optimization. Organizations can eliminate inefficiencies, reduce costs, and improve employee performance by automating and optimizing workflows. One specific application of this is in customer service, where AI-powered chatbots can handle simple customer queries and seamlessly escalate more complex issues to human agents.
Building Workforce Resilience Amid Automation and AI Changes
As Generative AI continues to evolve, its impact on the workforce remains uncertain. Even so, the debate around its application in the workforce serves as a reminder that technological progress is an opportunity for evolution, adaptation, and innovation. Companies must analyze their workforces, identify core tasks, and customize their workforce strategies, considering potential Generative AI use cases and industry context. Aura's workforce analytics platform can help users understand the shifts in a particular company or industry by making workforce data & insights more accessible. With its growing number of datasets, covering almost a billion professionals worldwide, Aura is building the largest workforce-specific dataset to date.
Ultimately, the success of integrating Generative AI into the workforce will depend on how organizations, policymakers, and individuals navigate the delicate balance between harnessing AI's potential and safeguarding the human workforce.