Augmentation vs. Automation: Key Strategies for Workforce Success
AI is reshaping the way work gets done. Rather than replacing humans, companies use AI tools to help their teams be more effective and productive. This shift isn't about making people obsolete but empowering them to do more and grow their capabilities.
Recent research from Accenture underscores this trend, revealing that companies leveraging generative AI and automation achieve 2.5x higher revenue growth and 2.4x greater productivity than their peers. The study found that 74% of companies report meeting or exceeding expectations with their AI investments, with 63% planning to further strengthen these capabilities by 2026. Organizations are accelerating performance gains across multiple functions without compromising human roles by focusing on AI-led processes that integrate human expertise.
AI automation is about enhancing human capabilities with smart tools, not taking away jobs. Businesses are seeing impressive gains by implementing AI that supports rather than replaces. Employees can complete tasks faster and with greater precision, leading to wins all around.
AI can tackle repetitive tasks, analyze massive datasets in moments, and even provide decision-making support. But AI shines brightest when it complements human abilities like creativity and judgment. Companies investing in AI for workplace efficiency are increasing productivity without downsizing. This strategy boosts output, supports talent retention, and fills skill gaps.
Want to see how AI can transform workplace productivity and talent strategies? Schedule a demo of Aura’s workforce intelligence platform today to unlock actionable insights.
Striking the Balance: Choosing AI Augmentation or Automation for Your Team
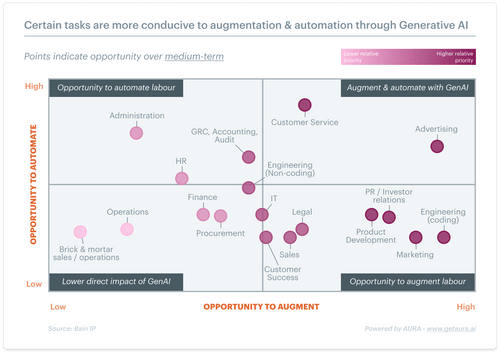
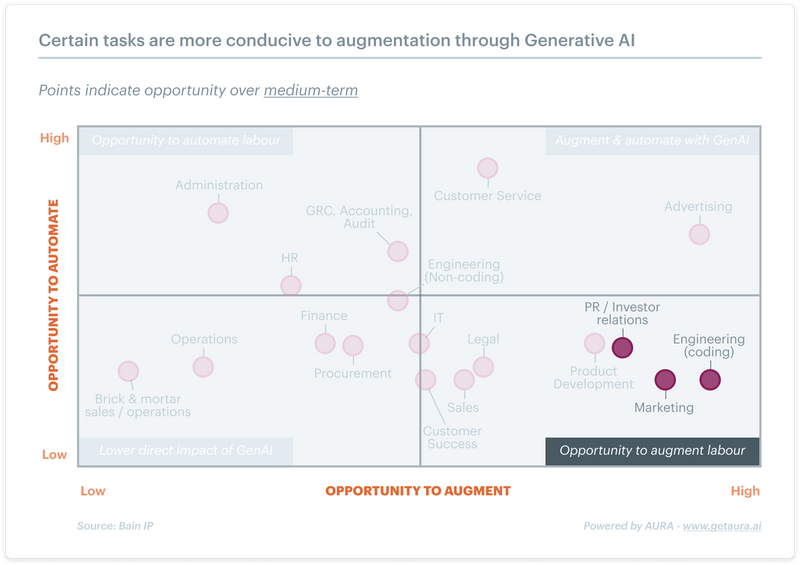
Generative AI (GenAI) is transforming workplace dynamics by offering pathways for both augmentation and automation. The key lies in striking a balance between these approaches, tailored to the unique needs of industries and organizations.
The following images analyze the most appropriate organizational functions to either augment or automate.

*Special thanks to Bain’s Gene Rapoport and Richard Lichtenstein for their materials and support in this article.
-
Augmentation: AI empowers human employees by enhancing productivity, streamlining workflows, and enabling innovation. For example, engineers can leverage GenAI for rapid data analysis, simulations, and design optimization, while marketing teams can use it to draft content and generate creative ideas.
-
Automation: Conversely, automation is ideal for repetitive, labor-intensive tasks. HR departments increasingly rely on AI for talent acquisition, payroll management, and employee tracking. Similarly, the accounting sector uses automation to simplify processes like invoice processing and bookkeeping, freeing professionals to focus on strategic activities.
-
Integration of Both Approaches: Many organizations combine augmentation and automation to harness each other's strengths. For instance, a healthcare provider might automate data analysis while relying on medical staff to make patient care decisions, blending efficiency with the human touch.
-
Future Workforce Strategies: Businesses must assess their workforce needs, identify tasks suited for GenAI, and address ethical concerns such as job displacement. By investing in upskilling programs and thoughtful planning, organizations can navigate the challenges of rapid technological change while preserving human creativity, empathy, and intuition.

Adopting GenAI isn't just about operational efficiency—it's about reimagining the future of work. Whether through augmentation, automation, or both, the integration of AI promises to revolutionize industries while requiring deliberate, human-centered strategies.
Emerging Trends: How AI Augmentation and Automation are Shaping the Workforce
AI is transforming how companies enhance efficiency and make the most of their talent. More and more organizations are turning to AI to support their workforce.
AI-powered data analytics deliver managers valuable insights, allowing them to improve team dynamics and performance. Meanwhile, employee sentiment analysis is gaining traction for leaders to gauge employee satisfaction and address concerns before they become issues.

Across sectors, from finance to healthcare, AI is making processes smoother and more effective. For instance, AI helps banks speed up risk assessment and fraud detection, allowing staff to focus on complex cases. Healthcare benefits, too, with AI speeding up radiology workflows, freeing doctors to spend more time with patients. In tech, AI assists developers by handling repetitive coding tasks, enabling them to focus on innovative solutions.
Surveys show that employees are eager to develop AI-related skills, yet training opportunities remain limited. Companies prioritizing AI training and upskilling will likely have a competitive advantage in retaining top talent.
AI technology is advancing quickly, and companies that stay ahead of these trends will be better positioned to lead.
Essential Skills for Thriving in AI-Augmented Workplaces
A new set of skills is essential to excel in an AI-augmented workplace. Professionals adept at working directly in AI and alongside AI are both in high demand.
AI-related job postings are growing 3.5 times faster than other roles, underscoring the increasing need for AI-aligned skills. Aura workforce analytics also found strong support for this claim, with AI making up a substantive part of all new software-related jobs.

Recent Data from Aura Shows AI Jobs Growing Throughout the Year as a Percentage of All Jobs Posted
Key high-income competencies include:
- Advanced analytics
- AI literacy
- Complex problem-solving
- Ethical AI implementation
- Data interpretation
Consultants are pivotal in helping organizations identify and develop these high-demand skills through workforce planning. Executives estimate that up to 40% of their workforce will require reskilling due to AI and automation. This presents a unique opportunity for organizations to optimize talent for the future.
Companies can stay agile and competitive in an evolving job market by focusing on AI-related skills.
Optimizing Workforce Performance: AI Benchmarking in Action
AI-powered benchmarking tools are revolutionizing how consultants help clients enhance performance through data insights.
AI benchmarking is helping optimize management decisions and track industry players team composition and workforces. In retail applications, consultants can analyze dynamic, real-time data to recommend optimal stock levels, reducing waste and maximizing sales.
AI insights improve production efficiency in manufacturing by comparing a client's output to industry standards. Financial firms leverage AI benchmarking to assess productivity, enabling consultants to suggest strategies for enhanced efficiency.
AI tools also help consultants make informed recommendations on operational cost management. They can identify overspending areas relative to competitors and propose targeted solutions, enhancing clients' financial performance.
Consultants also use AI to improve talent allocation, analyzing workforce trends across sectors to advise on optimal staffing levels. AI-enhanced KPIs offer detailed insights into current and future performance, providing clients a clearer picture of their market position.
AI's Influence on Software Engineering and the Technology Function
The rapid integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into software development is reshaping the profession, presenting both challenges and opportunities for software engineers and organizations.
Evolving Skill Requirements
AI-powered coding assistants, such as GitHub Copilot and Amazon CodeWhisperer, are automating routine coding tasks, enabling developers to focus on more complex problem-solving and strategic planning. This shift necessitates a broader skill set, emphasizing critical thinking, system architecture, and effective communication. As AI handles repetitive tasks, engineers are expected to oversee AI-driven workflows and address higher-level challenges.
Impact on Entry-Level Positions
AI tools' automation capabilities influence hiring trends, particularly for entry-level positions. Some organizations anticipate a reduced need for junior developers, as AI can perform tasks traditionally assigned to less experienced engineers. This evolution underscores the importance of emerging professionals adapting by acquiring skills that complement AI technologies, thereby enhancing their employability in an AI-augmented environment.
Continued Demand for Experienced Engineers
Despite these changes, according to Aura's data, the expertise of seasoned software engineers remains crucial. Their ability to design complex systems, make informed decisions, and provide mentorship is invaluable. While AI is a powerful tool to boost productivity, it cannot replicate the nuanced understanding and innovative thinking that experienced engineers contribute. Consequently, professionals who integrate AI effectively into their workflows will likely excel in this evolving landscape of greater automation.
How AI Automation Drives Operational Efficiency and Reduces Costs
AI is broadly reshaping operational efficiency and cost management across various industries, giving consultants powerful tools to streamline clients’ processes.
AI optimizes supply chains and reduces transportation costs by analyzing logistics shipping routes. For example, using AI-powered route planning, a major retailer reduced fuel consumption by 15%.
Healthcare facilities save millions using AI in predictive maintenance, preventing equipment breakdowns. Retailers use smart inventory management to reduce overstocking and stockouts, boosting profit margins.
Consultants harness AI insights to pinpoint inefficiencies in client workflows, leading to substantial cost savings. Common AI-driven improvements include:
-
Resource allocation
-
Reducing production waste
-
Enhancing energy efficiency
-
Optimizing staffing levels
AI chatbots handle routine inquiries in customer service, freeing human agents to focus on complex issues. This approach improves response times, enhances customer satisfaction, and cuts labor costs.
Shaping the Future: AI Augmentation’s Role in Talent Development
As AI technologies advance, businesses increasingly balance AI augmentation vs. automation to optimize their workforce without compromising the human element. AI isn’t just about replacing human employees; it’s about enhancing human intelligence with new tools that boost productivity and effectiveness across industries.
With AI augmentation, companies empower their teams to achieve more by taking over routine tasks like data entry, issue resolution, and repetitive tasks, allowing workers to focus on higher-level, strategic responsibilities that require human cognition and creativity.
Across various sectors, AI systems are handling vast datasets, providing insights and data-driven opportunities that drive smarter decision-making. Large language models enable talent acquisition teams to streamline the recruitment process, targeting candidates with specialized skills efficiently, which not only accelerates hiring processes but also supports job creation by aligning talent with evolving market needs.
For a specific example of this, Chipotle recently implemented Paradox’s AI hiring platform to speed up its recruitment process, taking over time-consuming administrative duties from restaurant managers. This move showcases how AI can optimize essential tasks, blending automation with support for roles previously handled by staff.
In fields such as medical diagnosis, virtual assistants and generative AI tools can process large amounts of data, assisting healthcare professionals in making timely and accurate assessments without replacing human intervention. Meanwhile, self-driving cars and automated logistics are examples of AI-powered system designs that benefit from a balance of automation and augmentation, where AI capabilities handle repetitive tasks while humans manage oversight, ensuring safety and flexibility.
AI’s impact extends to online platforms where AI-driven analytics aid companies in improving user satisfaction and economic value by predicting trends and enhancing services. This fusion of AI augmentation and human labor doesn’t just promote efficiency; it also builds a competitive advantage for businesses that leverage AI technologies to retain the human workforce while maximizing potential benefits.
The future of work lies in technology that enables human employees to thrive alongside automated solutions, emphasizing better outcomes through human-machine collaboration. This strategy fosters adaptability, encourages informed decisions, and opens doors for workers to develop high-value skills that keep them agile in a rapidly changing job market. In essence, AI augmentation is reshaping the workplace, helping businesses unlock productivity and innovation without compromising the human touch.
Data-Driven Strategies for AI Augmentation and Workforce Optimization
AI is transforming consulting approaches to workforce optimization. By leveraging workforce resilience data, consultants can offer meaningful insights to clients.
These data-driven augmentation strategies give clients a competitive advantage by maximizing productivity and flexibility. AI-driven consulting helps businesses balance automation with human expertise for optimal results. By guiding clients through this complex landscape, consultants can help them achieve long-term success and leverage the full potential of their workforce.
Unlock your team’s potential with Aura’s workforce intelligence platform. Book your free demo today and embrace the future of work.